Scaffolding Erection and Dismantling Procedure
Scaffolding is a critical temporary structure used to provide safe access and working platforms at height. While scaffolds support many construction and maintenance activities, they also present serious hazards if not erected or dismantled correctly. A large number of fall-from-height and collapse incidents occur during scaffolding erection and dismantling, making these phases the most dangerous in the scaffold lifecycle.
A well-defined Scaffolding Erection and Dismantling Procedure ensures that scaffolds are assembled safely, used correctly, and removed without exposing workers to unnecessary risks. This article provides a detailed, step-by-step explanation of safe erection and dismantling procedures, including planning, safety controls, inspections, and best practices.
Why Proper Scaffolding Procedures Are Critical
Scaffold accidents can result in:
- Fatal falls from height
- Scaffold collapse
- Falling objects injuring workers below
- Structural failure due to overloading
- Legal penalties and project delays
Following a proper procedure ensures compliance, protects workers, and maintains structural integrity throughout the scaffold’s use.
Legal and Safety Requirements for Scaffolding
Most national and international safety regulations require that:
- Scaffolds are erected and dismantled by competent persons
- Risk assessments are conducted
- Fall protection is provided during erection and dismantling
- Scaffolds are inspected and tagged before use
Failure to comply can lead to severe legal and safety consequences.
Roles and Responsibilities in Scaffolding Work
Management Responsibilities
- Provide approved scaffold materials
- Ensure competent scaffolders are appointed
- Provide training and fall protection equipment
- Approve scaffold plans and permits
Scaffold Supervisor Responsibilities
- Supervise erection and dismantling
- Ensure procedures are followed
- Verify scaffold stability
- Arrange inspections and tagging
Scaffolders Responsibilities
- Follow approved erection sequence
- Use PPE and fall protection
- Report damaged components
- Maintain safe work practices
Safety Officer Responsibilities
- Review risk assessments
- Audit scaffold safety
- Verify compliance with standards
- Support training and inspections
Pre-Erection Planning for Scaffolding
Scaffold Design and Selection
Before erection begins, determine:
- Type of scaffold required
- Height and load capacity
- Duration of use
- Access and egress requirements
- Environmental conditions
Complex scaffolds may require engineered drawings.
Risk Assessment and Permit to Work
A task-specific risk assessment must identify:
- Fall hazards
- Ground stability risks
- Falling object hazards
- Weather-related risks
For high or complex scaffolds, a Permit to Work must be issued.
Inspection of Scaffold Materials
All components must be inspected before use.
Check for:
- Bent or corroded tubes
- Cracked or damaged planks
- Defective couplers
- Missing components
Damaged materials must be removed from service.
Ground Preparation
Scaffold foundations must be strong and level.
Ensure:
- Firm ground conditions
- Use of sole boards and base plates
- Proper drainage to avoid settlement
Poor foundations are a major cause of scaffold collapse.
Personal Protective Equipment for Scaffolders
Mandatory PPE includes:
- Safety helmet with chin strap
- Full-body harness with lanyard
- Safety shoes with anti-slip soles
- Gloves
- High-visibility vest
Fall protection is essential during erection and dismantling.
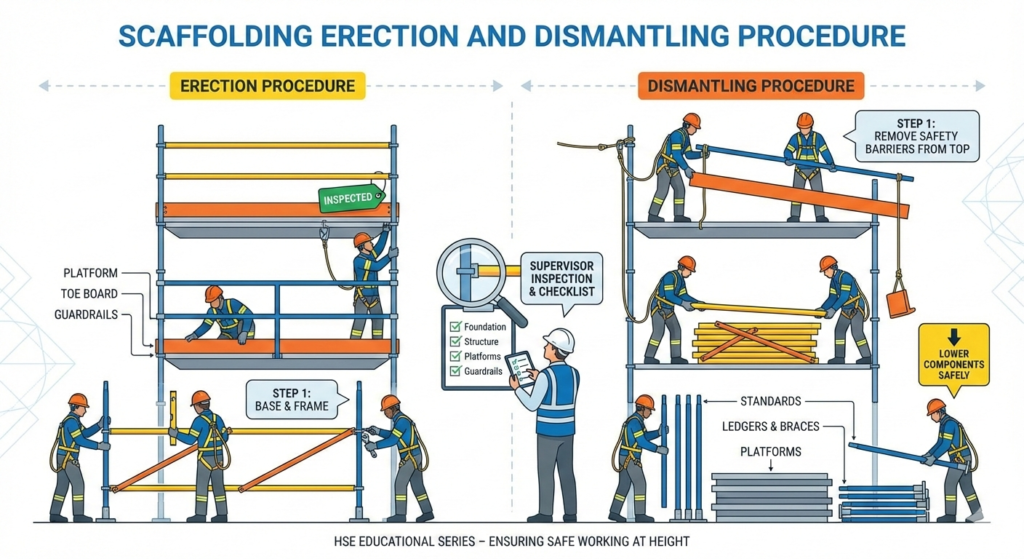
Scaffolding Erection Procedure
Step 1: Establish the Scaffold Base
- Mark the scaffold layout
- Place sole boards on firm ground
- Install base plates on sole boards
- Ensure bases are level and aligned
The base determines overall scaffold stability.
Step 2: Install Standards (Vertical Members)
- Fix standards vertically on base plates
- Maintain correct spacing as per design
- Ensure standards are plumb
Standards transfer load to the ground.
Step 3: Fix Ledgers and Transoms
- Connect ledgers horizontally between standards
- Install transoms at right angles
- Secure all connections with approved couplers
These components provide structural strength.
Step 4: Install Bracing
- Fix diagonal and horizontal braces
- Ensure bracing is installed as per design
Bracing prevents sway and collapse.
Step 5: Progressive Platform Installation
- Install working platforms as erection progresses
- Use scaffold planks or steel decks
- Secure platforms properly
Workers should not stand on incomplete decks.
Step 6: Install Guardrails and Toe Boards
- Install top and mid guardrails
- Fix toe boards at platform edges
Edge protection must be installed as early as possible.
Step 7: Provide Safe Access
- Install ladders or stair towers
- Secure access points
- Ensure safe entry and exit
Climbing on scaffold frames is prohibited.
Step 8: Implement Fall Protection During Erection
- Use advance guardrail systems or
- Use harnesses connected to secure anchor points
Scaffolders are exposed to fall risk during erection.
Step 9: Complete Scaffold and Final Inspection
- Verify all components are installed
- Check alignment and stability
- Ensure load capacity is not exceeded
Step 10: Scaffold Tagging and Handover
- Inspect scaffold by competent person
- Attach scaffold tag
- Green tag indicates safe for use
No one should use an untagged scaffold.
Scaffolding Dismantling Procedure
Dismantling is as hazardous as erection and must follow a controlled process.
Pre-Dismantling Preparation
- Obtain dismantling permit if required
- Ensure scaffold is no longer in use
- Barricade the area below
- Inspect scaffold condition
Step 1: Remove Materials and Debris
- Clear tools and materials from platforms
- Ensure platforms are empty
Step 2: Remove Access Components
- Remove ladders or stair towers last used
- Maintain safe access until dismantling is complete
Step 3: Remove Guardrails and Toe Boards
- Remove edge protection systematically
- Use fall protection during removal
Step 4: Remove Platforms
- Remove planks or decks level by level
- Do not throw materials down
Step 5: Remove Bracing, Transoms, and Ledgers
- Dismantle in reverse order of erection
- Maintain stability at all times
Step 6: Remove Standards
- Remove standards last
- Ensure no load remains
Step 7: Lower and Stack Materials Safely
- Use ropes or mechanical aids
- Stack materials neatly
- Inspect components for damage
Safety Precautions During Erection and Dismantling
- Never work in high winds or rain
- Never overload scaffolds
- Do not modify scaffold without approval
- Maintain exclusion zones below
- Use proper communication
Common Causes of Scaffolding Accidents
- Missing guardrails
- Inadequate bracing
- Poor foundations
- Untrained scaffolders
- Ignoring procedures
Inspection and Maintenance Requirements
Scaffolds must be inspected:
- Before first use
- Daily before work
- After modification
- After adverse weather
Records of inspection must be maintained.
Best Practices for Safe Scaffolding Work
- Use competent scaffolders only
- Follow approved designs
- Implement fall protection early
- Conduct regular training
- Enforce tagging systems
Conclusion
The Scaffolding Erection and Dismantling Procedure is a critical safety process that directly affects worker safety at height. By following a structured, step-by-step approach — supported by planning, training, supervision, and inspection — organizations can significantly reduce scaffold-related accidents.
Remember, most scaffold accidents occur during erection and dismantling. Doing these tasks safely is not optional — it is essential.
For checklist and templates visit The HSE Tools.
Scaffold Components and Types Explained
Roof Work Safety: Do’s and Don’ts
Common Causes of Falls and Their Prevention
Permit to Work for Height-Related Activities
Scaffold Erection and Dismantling Safety Procedures
FAQs
1. Who is allowed to erect and dismantle scaffolding?
Only trained and competent scaffolders.
2. Is fall protection required during scaffold erection?
Yes, fall protection is mandatory.
3. When should scaffolds be inspected?
Before use, daily, and after any modification.
4. Can scaffolding be dismantled in any order?
No, it must be dismantled in reverse order of erection.
5. What is the purpose of scaffold tagging?
To indicate whether a scaffold is safe for use.