Electrical Work HIRA – Top 10 Critical Hazards and the Ultimate Safety Blueprint
📘 Introduction
Electrical work is essential in construction, manufacturing, and maintenance—but it’s also one of the most hazardous. From arc flashes to electric shocks, working with energized equipment demands a proactive risk assessment approach. That’s where a well-prepared Electrical Work HIRA (Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment) becomes crucial.
⚠️ According to OSHA, electrical hazards cause hundreds of deaths and thousands of injuries annually—many of which are preventable with proper controls and training.
This guide offers a comprehensive Electrical Work HIRA framework that aligns with OSHA 29 CFR 1910 Subpart S and NFPA 70E.
🎯 Objective of Electrical Work HIRA
The purpose of this Electrical Work HIRA is to:
- Identify electrical hazards during live or de-energized tasks
- Assess risk severity and likelihood
- Implement control measures to mitigate the risks
- Ensure compliance with global safety standards
- Promote a culture of proactive hazard management
⚡ Scope of Electrical Work
The following tasks are covered under this Electrical Work HIRA:
- Panel board maintenance
- Cable termination and jointing
- Electrical equipment installation
- Circuit testing and commissioning
- Energized systems troubleshooting
- Use of power tools and extension cords
These activities present a wide range of hazards, all of which should be evaluated using this Electrical Work HIRA.
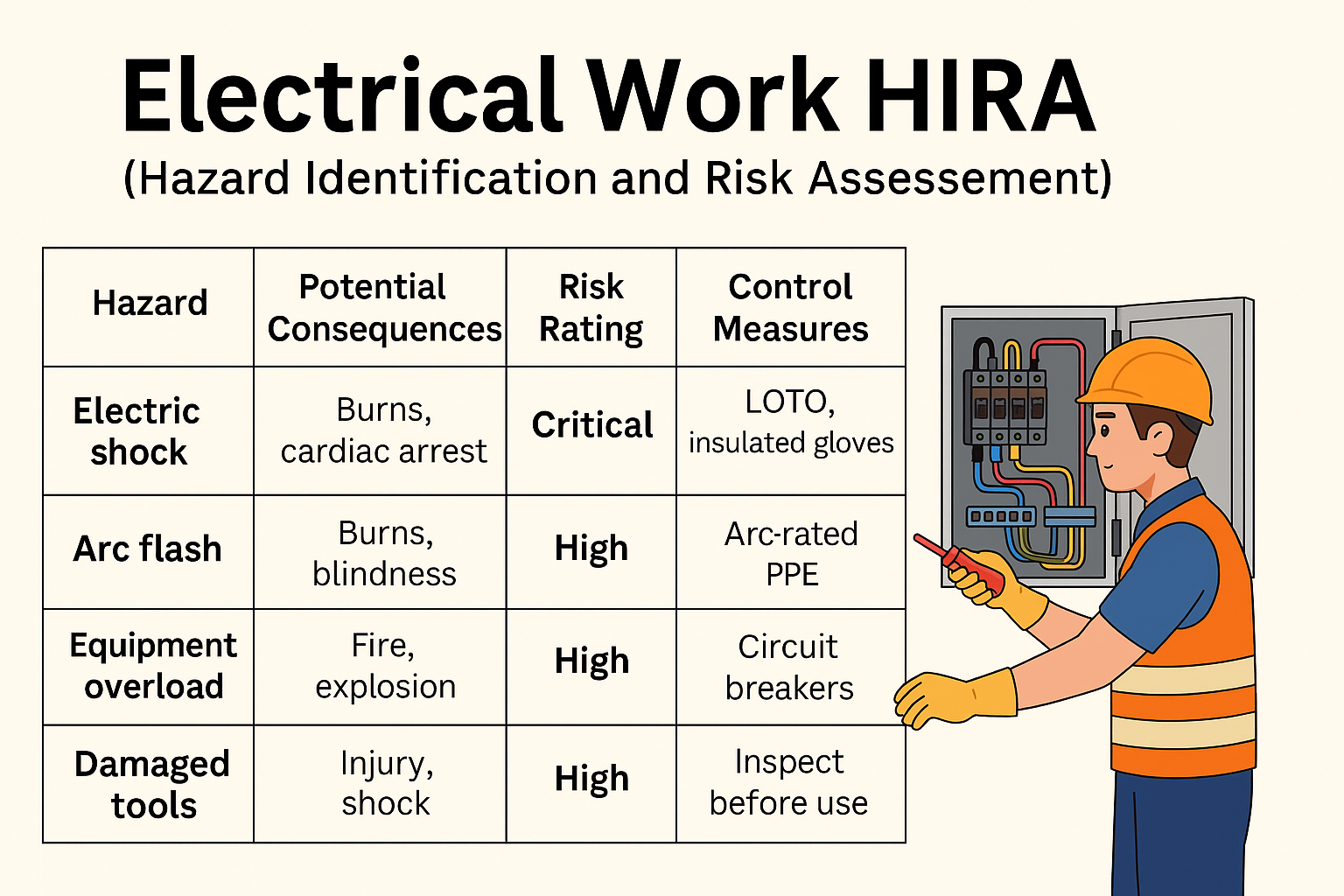
⚠️ Top 10 Hazards in Electrical Work HIRA
| # | Hazard | Consequences | Risk Rating |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Electric shock | Burns, cardiac arrest, death | Critical |
| 2 | Arc flash/blast | Severe burns, blindness | Critical |
| 3 | Equipment overload | Fire, explosions | High |
| 4 | Poor grounding | Shock, equipment damage | High |
| 5 | Wet conditions | Increased shock risk | High |
| 6 | Contact with live wires | Fatal injuries | Critical |
| 7 | Inadequate PPE | Exposure to current or flash | High |
| 8 | Use of damaged tools | Accidental shocks | Medium |
| 9 | Incomplete lockout/tagout | Unexpected energization | Critical |
| 10 | Unqualified workers | Improper handling, accidents | High |
A well-structured Electrical Work HIRA will ensure these hazards are anticipated and mitigated.
🔎 Risk Assessment Matrix
| Hazard | Likelihood (L) | Severity (S) | Risk Score | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electric shock | 4 | 5 | 20 | Critical |
| Arc flash | 3 | 5 | 15 | High |
| Overload | 3 | 4 | 12 | High |
| Contact with live wire | 3 | 5 | 15 | Critical |
| Improper grounding | 3 | 4 | 12 | High |
🛠️ Control Measures in Electrical Work HIRA
🔹 Engineering Controls
- Use Residual Current Devices (RCDs) or GFCIs
- Ensure proper circuit breakers and fuses are installed
- Provide insulating mats and tools
- Install clear electrical warning signs and covers
- Use explosion-proof electrical fixtures in hazardous zones
🔸 Administrative Controls
- Implement Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) procedures
- Issue Permit-to-Work (PTW) for energized systems
- Conduct job-specific safety training
- Supervise tasks involving high-voltage equipment
- Carry out toolbox talks on electrical safety
- Maintain updated Electrical Work HIRA for each location
👷 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Insulated gloves and boots
- Arc-rated face shields and balaclavas
- Flame-resistant (FR) coveralls
- Safety goggles and ear protection
- Voltage-rated tools
All PPE must be documented in the Electrical Work HIRA and checked before use.
📋 Safe Work Procedure (SWP)
✅ Before Work
- Perform a risk assessment using this Electrical Work HIRA
- Check equipment and tools for defects
- Ensure Lockout/Tagout has been applied
- Test circuits with appropriate voltage detectors
- Barricade the work area and place danger signage
- Assign a qualified electrician to supervise
✅ During Work
- Maintain safe distances from energized components
- Follow PTW instructions and LOTO sequence
- Use insulated tools only
- Avoid distractions and multitasking
- Ensure constant communication within the team
✅ After Work
- Re-test circuit before re-energizing
- Remove LOTO tags only with authorized approval
- Close work permits and update Electrical Work HIRA log
- Return all tools and PPE to designated locations
- Report near-misses or anomalies
👥 Roles and Responsibilities
| Role | Responsibility |
|---|---|
| Electrician | Execute job as per Electrical Work HIRA |
| Safety Officer | Ensure permit process, audits, and training |
| Supervisor | Approve permit, validate controls |
| Permit Issuer | Review LOTO and energy isolation steps |
| Helper | Support with tools and maintain safe zone |
🆘 Emergency Preparedness
- Install nearby Emergency Stop switches
- Maintain First Aid kits with burn and shock treatment supplies
- Train team in CPR and electrical rescue procedures
- Keep emergency contact details posted on electrical panels
- Conduct mock drills every 6 months for electrical incidents
🔥 Note: A single arc flash can reach temperatures of 35,000°F — hotter than the surface of the sun. Never bypass your Electrical Work HIRA.
📊 Monitoring and Audits
- Daily inspection of cables and tools
- Monthly review of electrical permits
- Quarterly Electrical Work HIRA updates
- Annual LOTO training and certification
- Supervisor spot checks during ongoing jobs
✅ Conclusion
A single mistake in electrical work can be catastrophic. The Electrical Work HIRA is a vital tool to prevent fatal outcomes and ensure compliance with safety regulations. It protects workers, assets, and operations by eliminating guesswork and enforcing proven safety strategies.
Whether you’re installing a circuit or testing high-voltage systems, never proceed without completing a detailed Electrical Work HIRA.
Top 10 Deadly Hazards in Confined Space Entry HIRA – Ultimate Safety Guide
Top 10 Critical Hazards in Lifting and Rigging Operations HIRA – Ultimate Safety Guide
Equipment Installation and Commissioning HIRA (Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment)
Shuttering and De-shuttering Work HIRA (Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment)
Road Cutting and Paving HIRA (Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment)