Fall Protection: Components and Inspections?
In the dynamic landscape of occupational safety, fall protection stands as a paramount concern for employers and employees alike. This article aims to unravel the intricacies of fall protection, specifically focusing on its components and the crucial aspect of inspections.
I. Introduction
A. Brief Overview of Fall Protection
Fall protection involves a series of preventive measures designed to mitigate the risk of falls in the workplace. Whether in construction, manufacturing, or any industry with elevated workspaces, safeguarding against falls is non-negotiable.
B. Importance of Fall Protection in Various Industries
The significance of fall protection spans across diverse sectors, as accidents resulting from falls can lead to severe injuries and even fatalities. Establishing robust fall protection measures is not just a legal requirement but a moral obligation for employers.
II. Components of Fall Protection Systems
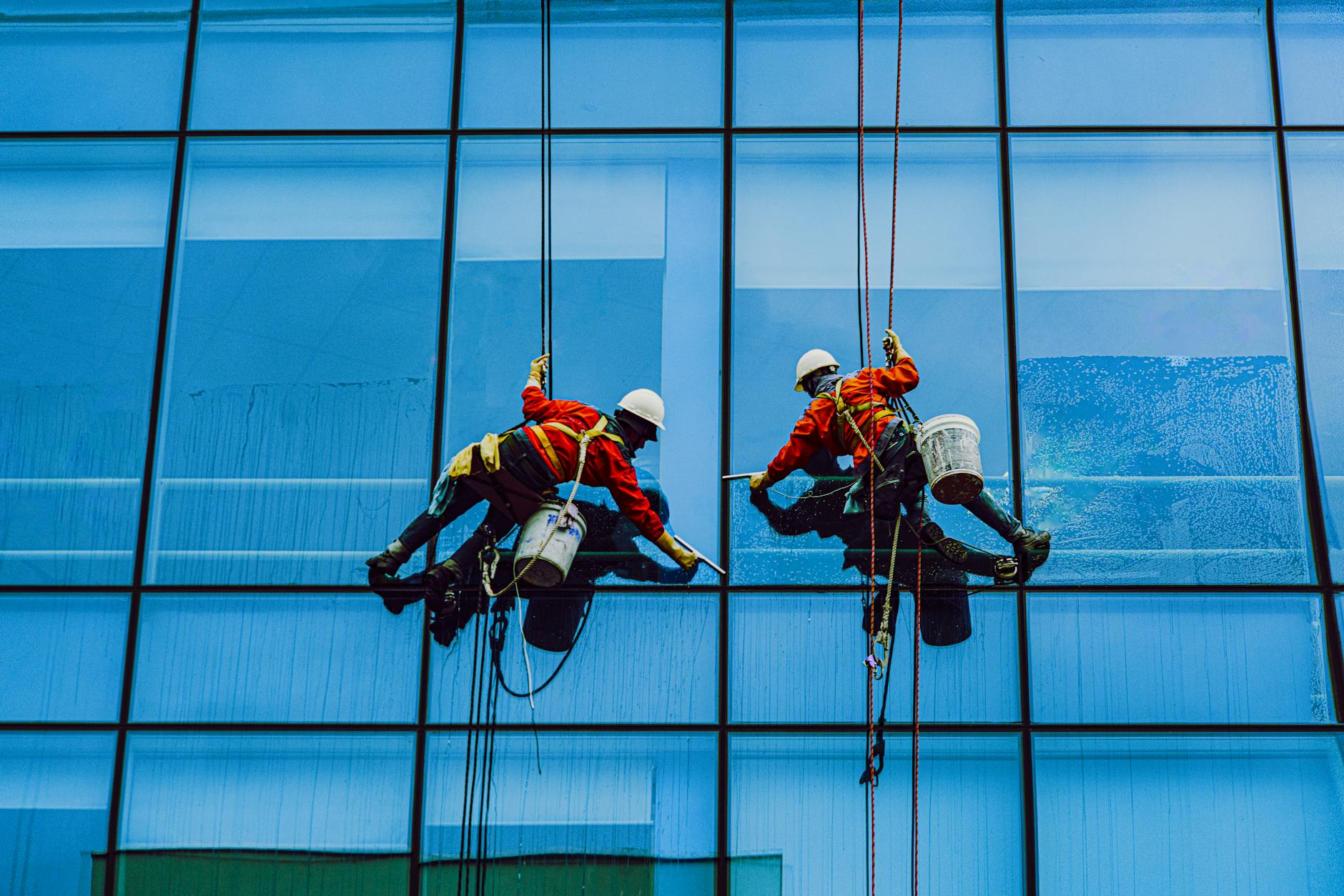
A. Harnesses and Lanyards
The cornerstone of fall protection, harnesses and lanyards provide a secure connection between the worker and the anchor point. Understanding the variations in harness designs and choosing the right lanyard is critical for effective protection.
B. Anchor Points
Identifying suitable anchor points is crucial for the success of a fall protection system. Whether fixed or temporary, anchor points should meet stringent safety standards to ensure the reliability of the entire system.
C. Lifelines and Deceleration Devices
Lifelines serve as a lifeline indeed, offering continuous protection as workers move at heights. Additionally, deceleration devices play a pivotal role in slowing down a fall, reducing the impact on the body.
III. Inspections and Maintenance
A. Regular Inspection Protocols
Routine inspections are the backbone of fall protection efficacy. Establishing a comprehensive inspection schedule ensures that every component is scrutinized for wear, tear, or potential defects.
B. Identifying Wear and Tear
Recognizing signs of wear and tear is a skill that inspectors must hone. Frayed edges, damaged stitching, or corrosion in metal components are red flags that demand immediate attention.
C. Importance of Timely Maintenance
Procrastination in maintenance can lead to catastrophic consequences. Timely repairs and replacements not only ensure the continued safety of workers but also extend the lifespan of the fall protection system.
Fall protection is a crucial aspect of workplace safety, especially in industries where employees are exposed to elevated work surfaces. Components and inspections play a vital role in ensuring the effectiveness of fall protection systems. Here's an overview:Components of Fall Protection Systems:
- Anchorage Points:
- Fixed points to which lifelines or lanyards are attached.
- Examples include roof anchors, beam anchors, and lifelines.
- Body Harness:
- Worn by workers to distribute fall forces throughout the body.
- Includes shoulder straps, chest straps, and leg straps.
- Lanyards:
- Connect the body harness to the anchorage point.
- Available in various lengths and materials.
- Self-Retracting Lifelines (SRLs):
- Automatically extend and retract to provide freedom of movement while maintaining fall protection.
- Guardrails:
- Physical barriers installed along the edges of elevated surfaces to prevent falls.
- Safety Nets:
- Placed below work areas to catch falling workers.
- Warning Lines:
- Visual indicators, often used in construction, to demarcate areas where fall protection is required.
- Fall Arrest Systems:
- Combines various components to arrest the fall of a worker and limit the forces applied to the body.
Inspections:
Regular inspections are crucial to ensure that fall protection systems are in good working condition. Inspections should be conducted before each use and at regular intervals, including:- Visual Inspections:
- Examine all components for signs of wear, damage, or deterioration.
- Check for loose stitching, frayed webbing, or corrosion on metal components.
- Functional Testing:
- Perform functional tests on self-retracting lifelines, ensuring they retract properly.
- Test anchorage points for stability and load-bearing capacity.
- Manufacturer Guidelines:
- Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for inspection and maintenance.
- Replace any components that do not meet specifications.
- Record Keeping:
- Maintain detailed records of inspections, repairs, and replacements.
- Document the date of inspection and the name of the inspector.
- Training:
- Ensure that workers are trained to recognize and report any issues with fall protection equipment.
- Provide regular training on the proper use and care of equipment.
- Compliance Checks:
- Ensure that the fall protection system complies with relevant safety standards and regulations.
By prioritizing the proper selection, use, and maintenance of fall protection components, workplaces can significantly reduce the risk of falls and enhance overall safety. Regular inspections are essential to identify and address potential issues before they compromise the effectiveness of the fall protection system.IV. Types of Fall Protection Systems
A. Passive Fall Protection
Passive fall protection includes guardrails, safety nets, and other mechanisms designed to prevent falls in the first place. These systems are static and do not require active engagement from the worker.
B. Active Fall Protection
Active fall protection involves equipment that requires user engagement, such as harnesses and lanyards. This dynamic approach allows for flexibility in various work environments.
C. Suspension Systems
In scenarios where a worker may fall, suspension systems provide a means to rescue and safely lower the individual to the ground. Proper training in the use of suspension systems is paramount.
V. Standards and Regulations
A. OSHA Regulations
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets the gold standard for fall protection regulations in the United States. Employers must adhere to OSHA guidelines to ensure compliance and avoid penalties.
B. ANSI Standards
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) plays a pivotal role in establishing safety standards. Familiarizing oneself with ANSI requirements is crucial for selecting, using, and maintaining fall protection equipment.
C. Industry-Specific Guidelines
Different industries may have unique challenges and requirements. Adhering to industry-specific guidelines ensures that fall protection measures are tailored to the nuances of the workplace.
VI. Training and Education
A. Importance of Proper Training
Having the right equipment is futile without proper training. Employers must invest in comprehensive training programs to ensure that workers understand how to use fall protection gear correctly.
B. Periodic Refresher Courses
Regular training refreshers are essential, given the evolving nature of work environments. Keeping workers updated on the latest safety protocols enhances their ability to navigate potential hazards.
C. Creating a Safety-Conscious Culture
Beyond training, fostering a culture where safety is a shared responsibility enhances overall workplace safety. When employees actively participate in creating a safe environment, the risk of accidents decreases significantly.
VII. Selecting the Right Fall Protection System
A. Assessing Workplace Hazards
A thorough risk assessment is the starting point for selecting the right fall protection system. Understanding the specific hazards unique to each workspace is essential for effective implementation.
B. Tailoring Solutions to Specific Industries
Not all fall protection systems are created equal. Tailoring solutions to the specific needs and challenges of different industries ensures a more precise and effective safety strategy.
C. Consultation with Safety Experts
When in doubt, seek expert advice. Safety professionals can provide invaluable guidance in selecting, installing, and maintaining fall protection systems that align with regulatory standards and industry best practices.
VIII. Addressing Common Misconceptions
A. Dispelling Myths About Fall Protection
Misconceptions can undermine the effectiveness of fall protection efforts. Addressing common myths, such as “fall protection is only for extreme heights,” fosters a more accurate understanding among workers.
B. Educating Workers on the Importance of Compliance
Compliance is not a burden but a shared responsibility. Educating workers on the importance of adhering to fall protection protocols creates a safer work environment for everyone.
IX. Employer Responsibilities
A. Providing Necessary Equipment
Employers bear the responsibility of providing high-quality fall protection equipment. Cutting corners on equipment quality jeopardizes the safety of the workforce.
B. Regular Safety Audits
Conducting regular safety audits ensures that fall protection measures are not only in place but also functioning optimally. Addressing any issues promptly prevents potential accidents.
C. Encouraging Open Communication
Creating an environment where workers feel comfortable reporting concerns or suggesting improvements fosters a culture of open communication. This transparency is essential for maintaining a proactive approach to safety.
X. Employee Responsibilities
A. Proper Use of Equipment
Training is not a one-time event. Employees must consistently use fall protection equipment according to guidelines, ensuring their own safety and the safety of their colleagues.
B. Reporting Defects or Concerns
Prompt reporting of defects or concerns with fall protection equipment is crucial. A swift response to reported issues prevents potential accidents and reinforces a commitment to safety.
C. Staying Informed About Safety Protocols
Knowledge is power when it comes to safety. Employees should stay informed about evolving safety protocols and take an active interest in maintaining a safe working environment.
XI. Cost-Benefit Analysis
A. Balancing Costs with Safety Benefits
While the initial cost of fall protection systems may seem significant, the long-term benefits far outweigh the expenses. A thorough cost-benefit analysis emphasizes the value of investing in safety.
B. Long-Term Savings Through Injury Prevention
Preventing injuries is not just about safeguarding human lives; it also translates into significant cost savings for employers. Fewer accidents mean reduced medical expenses, workers’ compensation claims, and potential legal liabilities.
XII. The Psychological Impact of Fall Protection
A. Reducing Worker Stress and Anxiety
Knowing they are protected creates a sense of security among workers, reducing stress and anxiety associated with working at heights. A psychologically safe workplace contributes to overall employee well-being.
B. Building Trust Between Employers and Employees
Investing in fall protection demonstrates a commitment to the well-being of the workforce. This commitment builds trust between employers and employees, fostering a positive workplace culture.
XIII. Conclusion
A. Recap of Key Points
Fall protection is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Understanding the components, inspections, and broader aspects of fall protection is crucial for creating a comprehensive safety strategy.
B. Encouragement for Continuous Improvement
The dynamic nature of workplaces demands continuous improvement in fall protection measures. Embracing new technologies, adhering to evolving standards, and prioritizing ongoing education contribute to a safer working environment.
OSHA Scaffold Guardrail Requirements
OSHA Stair Handrail Requirements
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the primary purpose of fall protection?
- Fall protection is primarily designed to prevent and mitigate the risks associated with falls from elevated workspaces, ensuring the safety of workers.
- How often should fall protection systems be inspected?
- Fall protection systems should undergo regular inspections, ideally before each use, and more comprehensive inspections on a scheduled basis, as outlined by safety regulations.
- Are there industry-specific guidelines for fall protection?
- Yes, various industries may have specific guidelines and regulations pertaining to fall protection. It’s crucial for employers to be aware of and adhere to these guidelines.
- How can employers create a safety-conscious culture among employees?
- Fostering a safety-conscious culture involves providing comprehensive training, encouraging open communication, and actively involving employees in the ongoing improvement of safety protocols.