Fall Protection: Equipment and Inspection
Introduction
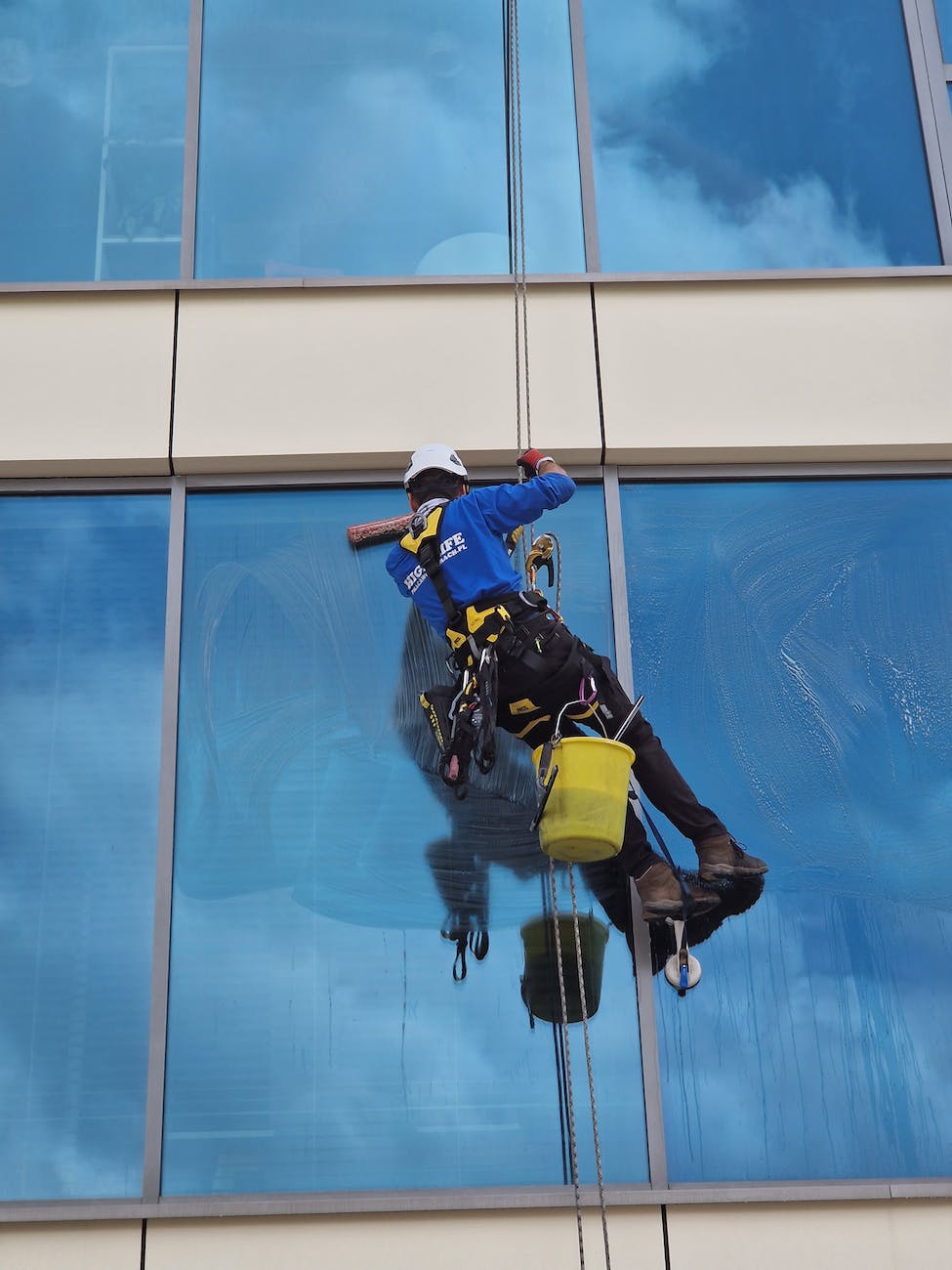
Fall protection is a critical aspect of workplace safety, especially in industries where employees are exposed to elevated work surfaces. This article delves into the importance of fall protection equipment and the significance of regular inspections to ensure the reliability and effectiveness of these safety measures.
Fall Protection Equipment
- Harnesses
- Purpose: Distributes fall forces over the thighs, pelvis, chest, and shoulders.
- Selection: Choose a harness appropriate for the work environment and potential fall hazards.
- Fit: Ensure a snug and secure fit, adjusting all straps according to manufacturer guidelines.
- Inspection: Regularly check for wear, tears, or damaged hardware. Replace any defective components.
- Lanyards and Lifelines
- Purpose: Connects the harness to an anchor point.
- Selection: Choose a lanyard with the appropriate length and shock-absorbing features.
- Fit: Verify the lanyard is correctly attached to the harness and anchor point.
- Inspection: Examine for fraying, cuts, or deformities. Inspect the energy absorber for signs of deployment or damage.
- Anchorage Points
- Purpose: Secure attachment points for lanyards and lifelines.
- Selection: Ensure anchor points meet the required strength and compatibility.
- Fit: Confirm proper attachment and structural integrity.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect for corrosion, loose bolts, or other signs of wear. Verify compatibility with the fall protection system.
- Retractable Lifelines
- Purpose: Automatically adjusts the lifeline’s length to prevent excessive slack.
- Selection: Choose the appropriate SRL based on the work environment and fall clearance requirements.
- Fit: Ensure correct attachment to the harness and anchor point.
- Inspection: Inspect for any signs of wear, malfunction, or damage. Check the braking system and retracting mechanism.
- Guardrails and Safety Nets
- Explanation of passive fall protection measures
- Installation and use of guardrails and safety nets for collective protection
- Safety Helmets
- The role of safety helmets in preventing head injuries during falls
- Types of helmets suitable for different work environments
- Rescue Equipment
- Overview of rescue equipment for prompt response to fall incidents
- Training on the use of rescue kits and devices for efficient retrieval
Importance of Fall Protection Equipment Inspection
- Ensuring Compliance
- Adherence to regulatory requirements for regular equipment inspection
- Avoidance of legal consequences by maintaining compliance with safety standards
- Identifying Wear and Damage
- Routine inspection for signs of wear, tears, or damage
- Early detection and replacement of compromised equipment to prevent failures
- Extending Equipment Lifespan
- Regular maintenance and inspection to extend the lifespan of fall protection equipment
- Avoiding premature replacements through proper care and timely repairs
- Verification of Functionality
- Confirming that equipment functions as intended
- Testing retractable lifelines, lanyards, and anchorage points to ensure proper response during a fall event
- Worker Confidence
- Boosting worker confidence in their safety equipment
- Ensuring that employees trust the reliability of their fall protection gear during daily tasks
- Enhancing Overall Safety
- Contributing to an overall culture of safety in the workplace
- Instilling a sense of responsibility for personal and collective safety among employees
Fall Protection Equipment Inspection Procedures
- Visual Inspection
- Regular visual checks for wear, tears, or damage
- Training workers on what to look for during visual inspections
- Functional Testing
- Periodic functional testing of retractable lifelines, lanyards, and anchorage points
- Ensuring that equipment responds appropriately to simulated fall scenarios
- Documentation of Inspections
- Maintaining detailed records of each inspection
- Documentation of inspection dates, findings, and actions taken for reference and compliance purposes
- Professional Inspections
- Scheduling professional inspections at regular intervals
- Engaging certified inspectors to assess the overall condition of fall protection equipment
- Worker Involvement
- Encouraging workers to report any concerns or issues with their fall protection equipment
- Fostering a collaborative approach to safety within the organization
- Manufacturer Guidelines:
- Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommended inspection intervals.
- Adhere to any specific maintenance or cleaning instructions.
- Storage:
- Store fall protection equipment in a clean, dry, and well-ventilated area.
- Protect equipment from exposure to sunlight, chemicals, and extreme temperatures.
- Retirement Criteria:
- Establish criteria for retiring equipment based on factors such as age, frequency of use, and exposure to environmental conditions.
- Retire any equipment that fails to meet safety standards.
- Training:
- Train users on how to perform pre-use inspections.
- Emphasize the importance of reporting any concerns or defects immediately.
Conclusion
In conclusion, fall protection equipment is a fundamental component of ensuring workplace safety in elevated work environments. Regular inspections play a crucial role in maintaining the reliability and effectiveness of this equipment. By emphasizing compliance, early detection of wear or damage, and a comprehensive inspection strategy, organizations can create a safer work environment and instill confidence in employees working at heights.
Work at Height Hazards and Control Measures
OSHA Scaffold Guardrail Requirements
OSHA Stair Handrail Requirements
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are the main components of fall protection equipment?
- Fall protection equipment includes harnesses, lanyards, lifelines, anchorage points, guardrails, safety nets, retractable lifelines, safety helmets, and rescue equipment.
- Why is the inspection of fall protection equipment important?
- Fall protection equipment inspection is crucial for ensuring compliance with regulations, identifying wear and damage, extending equipment lifespan, verifying functionality, boosting worker confidence, and enhancing overall workplace safety.
- What are some common types of fall protection equipment?
- Common types of fall protection equipment include full-body harnesses, lanyards, lifelines, anchorage points, guardrails, safety nets, retractable lifelines, safety helmets, and rescue equipment.
- How often should fall protection equipment be inspected?
- Fall protection equipment should be inspected regularly, with intervals determined by regulatory requirements and the manufacturer’s recommendations. Visual inspections may be more frequent, while professional inspections occur at scheduled intervals.
- What are the key procedures for inspecting fall protection equipment?
- Fall protection equipment inspections involve visual checks for wear and damage, functional testing of critical components, documentation of inspections, periodic professional inspections, and encouraging worker involvement in reporting concerns or issues with their equipment.