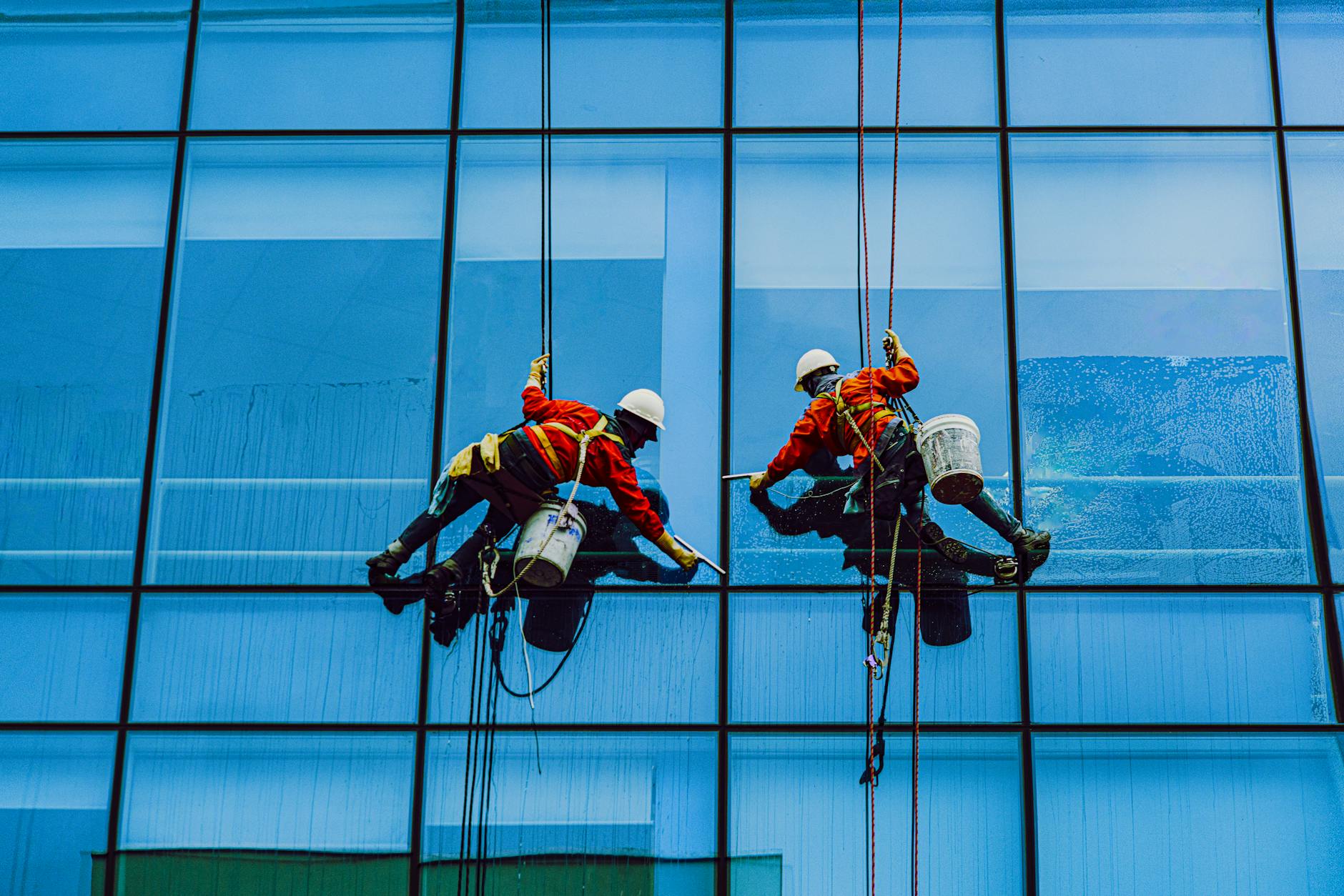

Personal Fall Arrest Systems: Safeguarding Workers through Proper Use and Inspection
Introduction
Working at heights is an inherent part of many industries, and ensuring the safety of workers in these environments is paramount. Personal Fall Arrest Systems (PFAS) are vital tools designed to protect workers from falls. This article explores the proper use and inspection of PFAS, emphasizing the crucial role they play in preventing accidents and safeguarding the well-being of those working at elevated heights.
Understanding Personal Fall Arrest Systems
- Components of PFAS
- Anchorage: The point of attachment for the PFAS.
- Body Support: Harness worn by the worker.
- Connecting Device: The lanyard or lifeline that links the body support to the anchorage.
- How PFAS Works
- Fall Arrest Function: In the event of a fall, the PFAS activates, arresting the fall and preventing the worker from hitting a lower level.
- Energy Absorption: Many PFAS incorporate energy-absorbing elements to reduce the impact force on the worker’s body.
Proper Use of Personal Fall Arrest Systems
- Harness Fitting and Adjustment
- Proper Sizing: Ensure each worker has a harness of the correct size to maximize effectiveness.
- Secure Fit: Adjust harness straps to achieve a snug and secure fit on the worker’s body.
- Anchorage Point Selection
- Strength and Stability: The chosen anchorage point must be strong and stable enough to support the potential fall force.
- Compatibility: Ensure compatibility between the connecting device and the anchorage point.
- Connecting Device Inspection
- Regular Checks: Inspect connecting devices for any signs of wear, damage, or malfunction regularly.
- Correct Length: Ensure the lanyard or lifeline is of the appropriate length to prevent striking a lower level in the event of a fall.
- Fall Clearance Calculation
- Calculate Minimum Clearance: Determine the minimum clearance required to prevent striking a lower level.
- Consider Swing Hazards: Account for potential swing hazards when calculating fall clearance.
Personal Fall Arrest Systems Inspection Guidelines
- Regular Equipment Inspections
- Pre-Use Checks: Conduct pre-use checks before each work shift to identify any immediate concerns.
- Scheduled Inspections: Perform more detailed inspections on a scheduled basis, following manufacturer guidelines.
- Inspecting Harness and Body Support
- Webbing and Stitching: Check for frayed webbing or damaged stitching on harnesses.
- Buckles and D-Rings: Inspect buckles and D-rings for signs of deformation or wear.
- Examining Connecting Devices
- Cable and Webbing Inspection: Ensure cables and webbing on lanyards and lifelines are free from cuts, abrasions, or other damage.
- Hardware Inspection: Check snap hooks and other hardware for proper functioning.
- Anchorage Point Assessment
- Structural Integrity: Confirm the structural integrity of the anchorage point.
- Secure Attachment: Ensure the anchorage point is securely attached to a structure capable of supporting the fall force.
Training and Education for Workers
- Proper Usage Training
- Initial Training: Provide comprehensive training for all workers on the correct usage of PFAS.
- Refresher Courses: Conduct regular refresher courses to reinforce safe practices.
- Emergency Procedures
- Rescue Planning: Develop and communicate emergency rescue procedures in the event of a fall.
- Training for Rescue: Ensure workers are trained in rescue techniques and equipment usage.
Conclusion
Personal Fall Arrest Systems are indispensable tools for ensuring the safety of workers operating at elevated heights. By understanding their components, following proper usage guidelines, conducting regular inspections, and providing thorough training, organizations can create a culture of safety that significantly reduces the risk of falls. Prioritizing the correct use and maintenance of PFAS not only safeguards workers but also contributes to a productive and secure work environment.
Work at Height Hazards and Control Measures
OSHA Scaffold Guardrail Requirements
OSHA Stair Handrail Requirements
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are the components of a Personal Fall Arrest System (PFAS)?
- The components include anchorage, body support (harness), and a connecting device (lanyard or lifeline).
- How does a PFAS work?
- In the event of a fall, a PFAS activates, arresting the fall and preventing the worker from hitting a lower level. Many PFAS also incorporate energy-absorbing elements to reduce impact forces.
- What are some key points for the proper use of PFAS?
- Ensure proper harness fitting and adjustment, select appropriate anchorage points, inspect connecting devices, and calculate fall clearance to prevent striking a lower level.
- How often should Personal Fall Arrest Systems be inspected?
- Conduct pre-use checks before each work shift and perform more detailed inspections on a scheduled basis, following manufacturer guidelines.
- Why is training important for workers using PFAS?
- Training is crucial for ensuring workers understand the proper usage of PFAS, including fitting, anchorage selection, and emergency procedures. Regular refresher courses help reinforce safe practices.
























A good lesson indeed.
May you assist with Rope Access Technician General Cleaner duties with Visa Sponsorship in the E.U.I have a great background in the Window and Structure Cleaning but I am willing to partake in other different Rope Access roles given the opportunity to learn.